
Bitcoin, the world’s first and most valuable cryptocurrency, has established itself as a robust store of value. However, as the ecosystem evolves, Bitcoin’s integration into broader DeFi has lagged behind other blockchain assets. While Ethereum and other smart contract platforms have seen explosive growth in DeFi, Bitcoin has largely remained idle, limited to its primary use case as a store of value.
Several prominent Bitcoin wrappers have emerged to bring Bitcoin into various blockchain ecosystems. Solutions like Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC), tBTC, sBTC, and newer ones like FBTC by Mantle and cbBTC by Coinbase have “bridged” Bitcoin into DeFi, offering varying mechanisms and utilities. These wrappers have proven that Bitcoin tokenization is both feasible and sustainable. The emergence of more Bitcoin wrappers and other tokenization solutions (with or without yield) highlights the critical timing and potential of such solutions in this cycle.
However, despite their benefits, all these wrappers share one major limitation: they are zero-yielding assets. This is where PBTC enters the picture – a yield-bearing variant of Bitcoin that could redefine Bitcoin’s role in the DeFi landscape.
The Bitcoin Wrapper Landscape
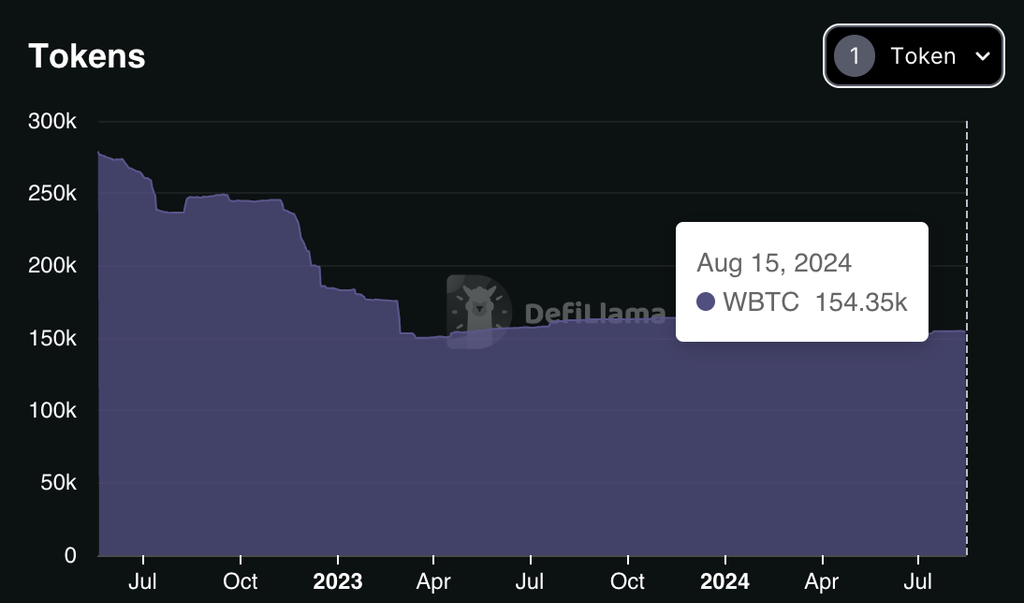
- wBTC Wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) is the most widely adopted Bitcoin wrapper, representing Bitcoin on the Ethereum network as an ERC-20 token. Offered by BitGo, wBTC provides significant liquidity and enables Bitcoin holders to participate in the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem. Despite its wide adoption (154.35k wBTC in circulation), wBTC operates under centralized custodianship, raising concerns about control and trust. Moreover, it offers no yield and has seen limited innovation in recent years, functioning primarily as a bridge to Ethereum.
- sBTC sBTC connects Bitcoin with smart contracts on the Stacks blockchain, bringing programmability to Bitcoin. It is pegged to Bitcoin and integrates well within the Stacks ecosystem, allowing Bitcoin to be used in new ways. However, sBTC faces challenges such as lower liquidity, slower transaction speeds, and the absence of yield generation, limiting its appeal.
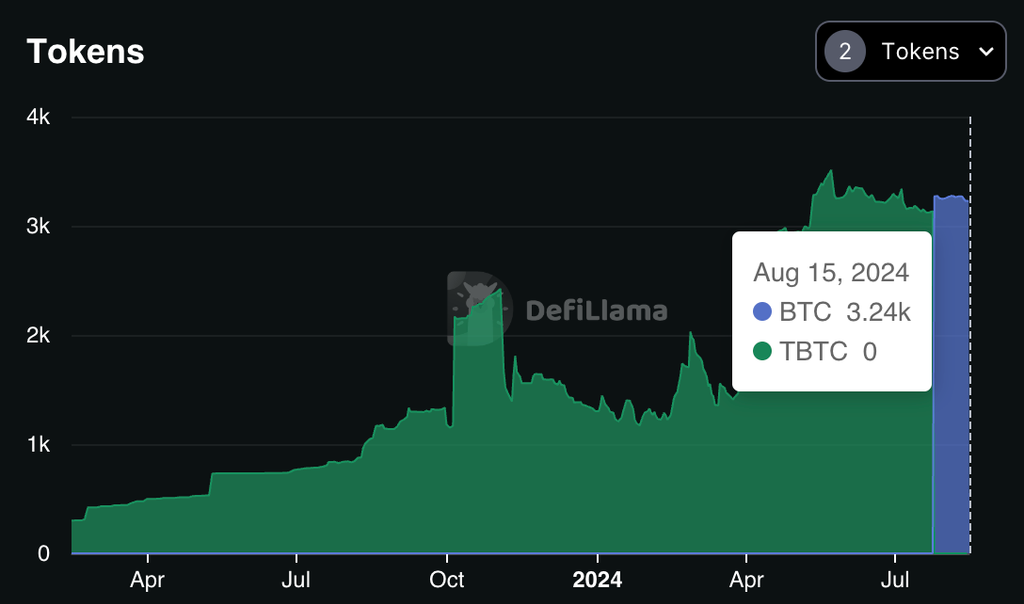
- tBTC tBTC is a decentralized Bitcoin wrapper on Ethereum, created by Threshold Network, offering a trustless bridge between Bitcoin and Ethereum. It stands out for its decentralized custody and multi-signer system, minimizing reliance on any single entity. Despite its innovative approach, tBTC has not achieved the same level of integration within the DeFi ecosystem as wBTC, largely due to lower liquidity (3.24k tBTC in circulation).
- FBTC FBTC is a new Bitcoin wrapper developed by Mantle and Antalpha Prime, live on Ethereum and Mantle networks. Designed with a 1:1 peg to Bitcoin, FBTC aims to enhance Bitcoin’s utility across multiple blockchain ecosystems. Although it is still in its early stages, FBTC is focused on scalability, interoperability, and yield generation, making significant efforts to bring DeFi partnerships and integrations.
- cbBTC cbBTC, offered by Coinbase, allows Bitcoin holders to use their BTC within the Coinbase ecosystem, including the Base network and supported DeFi protocols. While cbBTC benefits from seamless integration with Coinbase’s infrastructure, it remains centralized and does not generate yield, limiting its overall utility for advanced users.

The Stagnation of Zero-Yield Bitcoin Wrappers
Bitcoin wrappers enable BTC holders to engage with DeFi protocols on various networks like Ethereum, Base, Mantle, Stacks, and more. By wrapping BTC into an ERC-20 token, these solutions unlock access to a broader range of financial tools, such as lending, borrowing, and liquidity provision. However, these assets generate no yield, with their value tied solely to the underlying Bitcoin, which remains dormant and unproductive.
This lack of yield is a significant drawback. In a space where yield farming, staking, and lending are core elements of DeFi's value proposition, zero-yielding assets are less attractive. While wBTC and its counterparts have facilitated Bitcoin holders’ participation in DeFi, they have not fully unlocked Bitcoin’s potential to contribute more meaningfully to the ecosystem.
Enter PBTC: A New Era of Yield-Bearing Bitcoin
PBTC aims to transform how Bitcoin interacts with the DeFi ecosystem by converting idle Bitcoin into a productive asset. A key value proposition of PBTC lies in its ability to accept existing Bitcoin wrappers as deposit collateral and issue yield-bearing PBTC in return. This model opens up new possibilities for Bitcoin holders, allowing them to turn passive assets into yield-generating ones without sacrificing Bitcoin's fundamental benefits.
How PBTC Works
PBTC leverages a collateralized system where users can deposit existing Bitcoin wrappers such as wBTC, sBTC, tBTC, FBTC, or cbBTC (in addition to native Bitcoin and Bitcoin LST/LRTs). These deposits serve as collateral to mint PBTC, which generates yield through various DeFi strategies. By incorporating yield generation directly into its design, PBTC addresses the limitations of traditional Bitcoin wrappers and offers a more comprehensive solution for Bitcoin holders.
Advantages of PBTC Over Traditional Bitcoin Wrappers
- Yield Generation: PBTC’s primary advantage is its ability to generate yield, actively working to produce returns, unlike traditional Bitcoin wrappers.
- Broader Utility: PBTC will be integrated with a wide range of DeFi protocols, offering more options for users to use PBTC to generate more income to their BTC holdings.
- Flexibility: By accepting multiple Bitcoin wrappers as collateral, PBTC is not limited to one ecosystem, allowing Bitcoin holders from various ecosystems to leverage their assets effectively.
- Enhanced Liquidity: The yield-bearing nature of PBTC is expected to attract increased liquidity, enhancing its value proposition for individual investors, institutional participants, and DeFi protocols alike.
Challenges and Considerations
While PBTC presents a promising solution, it also encounters challenges common to the space that require careful management:
- Custodial Risk: The reliance on custodians introduces risks, such as accessibility issues, operational challenges during exchange failures, and potential insolvency.
- Smart Contract Risk: PBTC’s dependence on smart contracts exposes it to vulnerabilities that could affect its security and stability.
- Collateral Risk: The integrity of liquid staking tokens (LSTs) and Bitcoin wrappers is crucial. A critical issue could lead to market-wide instability, impacting PBTC’s backing value.
- Complexity: Yield-bearing mechanics and collateralization add complexity, which might deter some users.
- Adoption and Network Effects: Building a robust ecosystem and gaining trust is essential. Competing against established wrappers like wBTC requires strategic partnerships and clear value differentiation.
Photon Labs actively monitors and mitigates these risks, maintaining contingency plans and systems designed to enhance PBTC’s integrity and resilience. These risk management strategies will be detailed in public documentation, ensuring transparency. Additionally, third-party risk assessors evaluate and improve PBTC mechanisms with each iteration.
The Future of Bitcoin in DeFi
PBTC represents a significant evolution in Bitcoin’s integration into the DeFi ecosystem. By turning Bitcoin into a yield-bearing asset, PBTC could attract more Bitcoin holders who have been hesitant to engage in DeFi due to the limitations of zero-yielding wrappers. As more Bitcoin holders seek to maximize their assets’ utility and income, PBTC is well-positioned to become a key player in the DeFi space.
While current Bitcoin wrappers provide essential utility by bringing Bitcoin into different blockchain ecosystems, they are hampered by their zero-yield nature. PBTC offers a compelling solution by enabling yield generation on deposited Bitcoin wrappers, creating a more dynamic and valuable asset for the DeFi ecosystem. As PBTC gains adoption, it has the potential to redefine how Bitcoin is utilized in DeFi, transforming Bitcoin from a mere store of value into a productive asset.

.png)


